[The following is the second part of a talk which was given virtually on 25 May 2021 at the United Services Institution of India to its faculty, and undergraduate and postgraduate students taking part in a summer internship programme at the Institution. The first part covered spacecraft, launchers and exploration aspects. This concluding part gives an insight into organisations, the NewSpace phenomenon, the militarisation of space including capabilities of global space powers, and a brief overview of India’s space security policy and capabilities.]
Organisations
DOS and ISRO
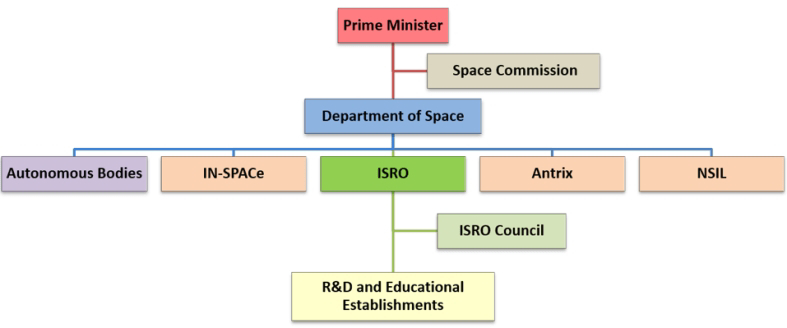
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is India’s national space agency, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the prime minister of India. ISRO is the primary agency in India to perform tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration and development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world which possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extra-terrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites.
To trace its history, the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within the DAE. In 1972, the Government of India set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS. Since then, it has been managed by the DOS, which governs various other institutions in India in the domain of astronomy and space technology.
ISRO is one of the largest space agencies in the world. It has completed 111 spacecraft missions, 80 launch missions and has placed in orbit 342 foreign satellites from 34 countries so far. ISRO’s launch systems have earned the reputation of being amongst the most reliable and cost-effective solutions in the world ].[The following is the second part of a talk which was given virtually on 25 May 2021 at the United Services Institution of India to its faculty, and undergraduate and postgraduate students taking part in a summer internship programme at the Institution. The first part covered spacecraft, launchers and exploration aspects. This concluding part gives an insight into organisations, the NewSpace phenomenon, the militarisation of space including capabilities of global space powers, and a brief overview of India’s space security policy and capabilities.]
Organisations
DOS and ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is India’s national space agency, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the prime minister of India. ISRO is the primary agency in India to perform tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration and development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world which possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extra-terrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites.
To trace its history, the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within the DAE. In 1972, the Government of India set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS. Since then, it has been managed by the DOS, which governs various other institutions in India in the domain of astronomy and space technology.
ISRO is one of the largest space agencies in the world. It has completed 111 spacecraft missions, 80 launch missions and has placed in orbit 342 foreign satellites from 34 countries so far. ISRO’s launch systems have earned the reputation of being amongst the most reliable and cost-effective solutions in the world [1].
Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL), Bengaluru is a wholly owned Government of India (GoI) enterprise under the administrative control of the DOS. Antrix was set up in 1992 as a marketing arm of ISRO for commercial exploitation of space products and transfer of technologies developed by ISRO. Another major objective was to facilitate development of space related industrial capabilities in India.
Antrix is engaged in providing space products and services to international customers worldwide. Antrix provides end-to-end solutions for many of the space products, ranging from simple subsystems to a complex spacecraft; space related services including remote sensing data service; transponder lease service; launch services; mission support services including establishment of ground infrastructure; and a host of consultancy and training services [2, 3].
Space India Limited (NSIL)
NSIL was set up by the DOS in March 2019. It aims to boost the growth of the Indian industry by taking up more technologically advanced space-related work. Its charter is to empower the industry in India. It facilitates transfer of technology from ISRO to the industry; provision of launch services for customer satellites; manufacture of SSLVs in collaboration with the private sector; production of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) through industry; and production and marketing of space-based services [4].
In general, while Antrix will facilitate ISRO’s commercial deals with foreign customers, NSIL will handle capacity building of local industry for space manufacturing.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (In-SPACe)
IN-SPACe is an independent nodal agency under Department of Space, establishment of which was announced as recently as Jun 2020. It is meant to act as a facilitator and regulator for Non-Governmental Private Entities (NGPEs). A licensing, authorisation, and supervisory regime for space activities has been put in place through IN-SPACe, as required vide the Outer Space Treaty, which India ratified in 1982 [5].
Mission Support Infrastructure
There are several establishments of ISRO which provide different services for satellite missions. Some of the major ones are [6]:-
Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh is the only spaceport of India.
Master Control Facility at Hassan in Karnataka and Bhopal in Madhya
Pradesh monitor and control all the communication and navigation satellites.
National Remote Sensing Centre at Hyderabad manages the remote sensing satellites, including dissemination of data.
ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network, Bengaluru is entrusted with providing tracking support for all the satellite and launch vehicle missions.




No comments:
Post a Comment