The US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has designed, and partnered with, two main agencies: the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Maryland manages the telescope development. It is operated by the Space Telescope Science Institute (JWST) on the Homewood campus of Johns Hopkins University. Its main contractor was Northrop Grumman. The telescope is named after James E. Webb, who was NASA's administrator from 1961 to 1968 during the Mercury, Gemini and Apollo programs.
The James Webb Space Telescope was launched on 25 December 2021 on an Ariane 5 rocket from Kourou, French Guiana, and reached the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point in January 2022. The first image of JWST was released to the public through a press conference. on 11 July 2022. The telescope is the successor to Hubble as NASA's flagship mission in astrophysics.
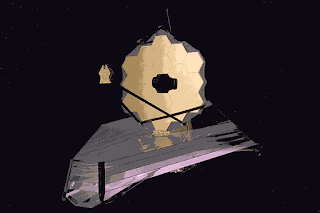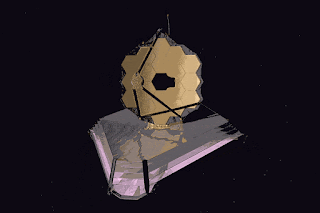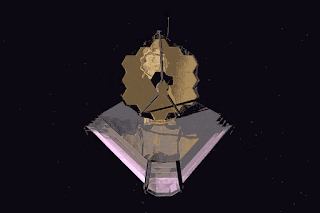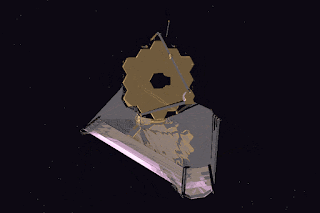
The primary mirror of JWST consists of 18 hexagonal mirror segments made of gold-plated beryllium, all these 18 hexagonal mirrors combined give JWST a light-collection area of approximately 25 square metres. Which is about six times that of Hubble. The Hubble telescope is based on ultraviolet rays (0.1 to 0.8 µm). JWST is based on infrared rays. It is positioned in solar orbit, about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. Where its five-layer sunshield protects it from being heated by the Sun, Earth and the Moon.
The initial design of this telescope was named Next Generation Space Telescope. which started in 1996. In 2005 it was redesigned to its present form. Its construction was completed at a total cost of US$10 billion.
It can detect objects 100 times fainter than Hubble, and objects much earlier in the history of the universe, at z≈20 (the cosmic timescale of about 180 million years after the Big Bang). can go back. For comparison, the earliest stars are believed to have formed between z≈30 and z≈20 (100–180 million years of cosmic time).
Infrared light passes through dust clouds more easily and cool objects like planets also emit infrared.
These infrared bands are difficult to study from the ground or by existing space telescopes such as Hubble.
Ground-based telescopes have to look through Earth's atmosphere. A variety of chemical compounds, such as water, carbon dioxide and methane are also present in Earth's atmosphere, greatly complicating the analysis.
The mass of the James Webb Space Telescope is about half the mass of the Hubble Space Telescope. The JWST has a 6.5-metre (21 ft)-diameter gold-coated beryllium primary mirror composed of 18 separate hexagonal mirrors. The mirror has a polished area of 26.3 m (283 sq ft), of which 0.9 m (9.7 sq ft) is obscured by secondary support struts, giving a total collection area of 25.4 m (273 sq ft). This is six times larger than the storage area of Hubble's 2.4-metre (7.9 ft) diameter mirror, which has a storage area of 4.0 m2 (43 sq ft). The mirror has a gold coating to provide infrared reflection and is covered by a thin layer of glass for durability.




No comments:
Post a Comment